
Empowering Data-driven Decisions: Self Service Reporting in a Dispersed Banking Environment
Table of Contents
In the ever-evolving banking industry, access to critical data is vital for informed decision-making. However, many banks face a common challenge – their data is dispersed across different systems, rather than residing within a single relational database. This fragmentation poses significant hurdles for self service reporting, where users require the ability to access and analyze data independently. In this blog, we will delve into the intricacies of self-service reporting in a banking environment with dispersed data, addressing its importance, requirements, success factors, growth considerations, common challenges, and suggested solutions.
Importance of Self Service Reporting
Self-service reporting empowers users by providing them with direct access to data, allowing for timely analysis and informed decision-making. It reduces dependency on IT teams for report generation, enables agile responses to changing business needs, and fosters a culture of data-driven decision-making throughout the organization.
Applicability and Limitations of Self Service Reporting
Self-service reporting is valuable in departments where quick access to data is crucial, such as risk management, compliance, and sales and so on. It is also beneficial for business users who require on-demand insights for operational decisions. However, caution should be exercised when dealing with sensitive data, as proper security measures and access controls must be in place to avoid unauthorized data exposure.
Consider these crucial points before building a Self Service Framework
To establish a robust self-service reporting framework, consider the following requirements:
Data Integration: Implement mechanisms to gather data from disparate systems and consolidate it in a central repository or data warehouse. However, many banks already have established data warehouses or BI system, makes it easy to plug the self-service tool to an existing repository.
User-Friendly Tools: Provide intuitive and easy-to-use reporting and analytics tools that empower users to explore and visualize data. Such as Tableau, Dundas BI and Google Charts etc. The full list of available BI tools self service capabilities click here.
Data Quality and Governance: Ensure data accuracy, consistency, and security through a strong data governance framework, including data validation, cleansing, and documentation.
Training and Support: Offer comprehensive training programs and ongoing support to users to maximize their proficiency in self-service reporting.
Key Points for Success in Self Service Reporting
User-Centric Approach: Its crucial to design self-service reporting framework with a deep understanding of user requirements and preferences. To make it intuitive and tailored to their needs, it is important to look at past data requests, consumption pattern and frequency of similar data. Involving users to define their desperate data requirements will have a direct impact on its success.
Data Accessibility: Ensure that data is easily accessible and available in real-time, enabling users to retrieve and analyze it when required.
Data Visualization: Incorporate visualizations and interactive dashboards to enhance data exploration and understanding.
Collaboration and Sharing: Enable users to collaborate, share insights, and promote knowledge exchange through features like data sharing and commenting.
Building for Growth and Sustainability
Designing the self-service reporting framework with scalability in mind, ensures it can handle increasing data volumes and user demands without compromising performance.
Evolving Banking industry leave its impact on data model, hence anticipate evolving business needs and adapt the framework. This flexibility allows easy integration of new data sources and evolving reporting requirements.
Establishing data governance practices in a self-service reporting environment promotes security, compliance, and data integrity. It helps protect sensitive information, ensures compliance with regulations and industry standards, maintains data accuracy and consistency, and establishes clear accountability and responsibility for data management. These practices contribute to the overall reliability, trustworthiness, and effectiveness of the self-service reporting environment within an organization.
Common Challenges & Solutions
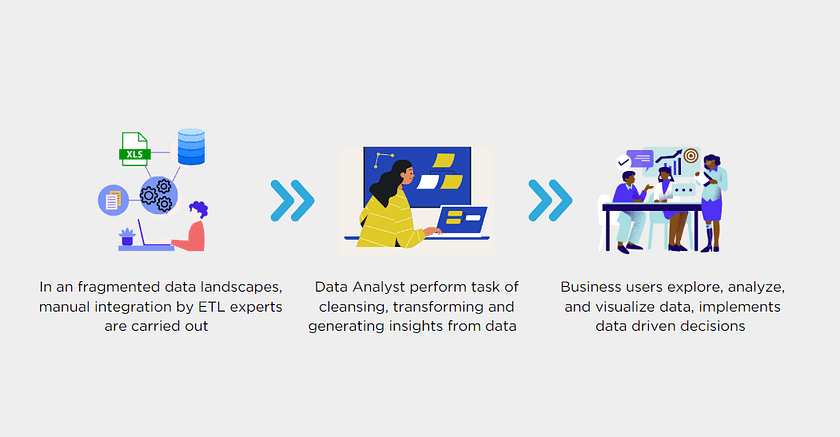
1. Dispersed Data: Data Accessibility is one of the most common issues. Users face challenges in locating and accessing relevant data due to its scattered nature. This leads to inefficiencies, delays, and increased reliance on IT support for report generation. Another usual issue is Data Consistency. Dispersed data increases the risk of inconsistencies and discrepancies, impacting the accuracy and reliability of self-service reports. Combining data from disparate sources becomes a complex task, often requiring manual effort and extensive data transformation.
Strategies to Overcome Dispersed Data Challenges:
- Implementing a data virtualization layer allows users to access and query data from various systems in real-time, providing a unified view without the need for data replication.
- Establishing a robust data governance framework ensures data quality, consistency, and security across multiple systems, enabling reliable self-service reporting.
- Deploying user-friendly analytics tools with intuitive interfaces empowers business users to explore, analyze, and visualize data independently, reducing dependency on IT teams.
- Leveraging APIs to integrate disparate systems enables seamless data flow, facilitating self-service reporting by consolidating information from multiple sources.
- Building a centralized data warehouse that aggregates data from various systems provides a single source of truth, simplifying self-service reporting and ensuring data consistency.
2. Data Quality: Establish data quality controls, including data validation rules and automated cleansing processes, to ensure accurate and reliable reporting.
3. User Adoption: Offer comprehensive training and ongoing support to promote user adoption and proficiency in self-service reporting tools.
4. Data Security: Implement robust access controls, encryption measures, and auditing mechanisms to protect sensitive data from unauthorized access
Dealing with strict data segregation policies
One of key issues occurs when sensitive data such as client-identification data is segregated in a CRM system and not stored in the data warehouse, there are still ways to utilize a BI tool for reporting and analysis while adhering to the strict data segregation policies. Here’s a possible approach:
Identify the reporting needs: Determine the specific reporting requirements and key performance indicators (KPIs) related to the client-sensitive data that need to be analyzed and reported on. Understand the objectives and insights desired from the segregated data.
Data integration: While the client-sensitive data may not be stored in the data warehouse, it is essential to integrate the relevant data from the CRM system with other non-sensitive data sources available in the data warehouse. This integration can be achieved through secure and controlled data pipelines or APIs.
Aggregate non-sensitive data: Utilize the BI tool to extract and aggregate non-sensitive data from the data warehouse that is relevant to the reporting needs. This data can include transactional data, demographic information, customer interactions, or any other non-sensitive data points that are required to provide context and support the analysis.
Combine with aggregated sensitive data: Apply appropriate aggregation and summarization techniques on the client-sensitive data within the CRM system to generate aggregated metrics and insights without exposing individual client-sensitive information. This could involve summarizing data at the account level, region level, or other relevant groupings while ensuring compliance with data protection regulations.
Create secure reports and dashboards: Utilize the BI tool’s report and dashboard creation capabilities to design secure and visually informative reports and dashboards based on the aggregated and combined data. Ensure that the reports and dashboards comply with data access restrictions and adhere to privacy regulations by carefully controlling user access rights and permissions.
Implement access controls: Configure the BI tool’s security settings to enforce strict access controls and permissions, ensuring that only authorized users have access to the reports and dashboards containing sensitive data. This involves setting up user roles, authentication mechanisms, and data-level security to limit access to the appropriate individuals or teams.
Monitor and audit: Regularly monitor and audit the usage of the BI tool and the reports containing sensitive data to ensure compliance with data segregation policies and regulations. Maintain an audit trail to track who accessed the reports, when, and for what purpose.
By following these steps, organizations can leverage a BI tool to gain insights from segregated sensitive data while maintaining strict data segregation policies. It allows for analysis and reporting on relevant aggregated data without compromising the security and privacy of the individual client-sensitive information.
